Modes of Ultrasound
A-mode (Amplitude mode)
Creates a one-dimensional graph that displays the amplitude of echoes as spikes along a baseline. It is primarily used in ophthalmology to measure distances within the eye or for precise targeting in therapeutic ultrasound.
While it is not commonly used for general imaging today, it is foundational for understanding how ultrasound data is acquired.

B-mode (Brightness mode)
The most common and standard ultrasound mode produces a two-dimensional grayscale image. The brightness of each pixel reflects the strength of the returning echoes. This mode is widely used for real-time visualization of anatomical structures in abdominal, obstetric, and other soft tissue imaging.

M-mode (Motion mode)
It captures motion along a single line of a B-mode image over time and displays this data as a graph, with motion on the y-axis and time on the x-axis. This method is particularly useful in cardiology for evaluating heart wall and valve motion, as well as in obstetrics for monitoring fetal heart rate.



Motion
Time
Doppler mode
-
Uses the Doppler effect to assess movement, typically blood flow, by detecting frequency shifts in returning echoes.
-
Provides information on direction and speed of blood flow:
-
Color Doppler: Shows blood flow direction and speed using colors (e.g., red for flow toward the probe, blue for flow away; lighter shades indicate faster flow).
-
Spectral Doppler: Graphically displays flow velocity over time.
-
Power Doppler: Sensitive to flow, regardless of direction, useful for detecting low-velocity flows.
-
Color Doppler
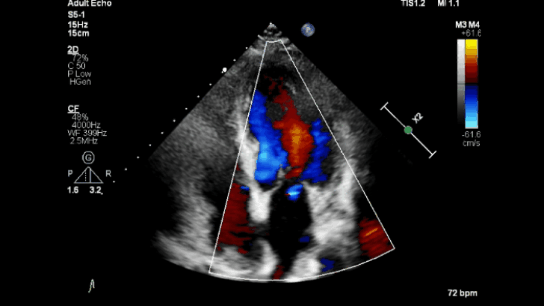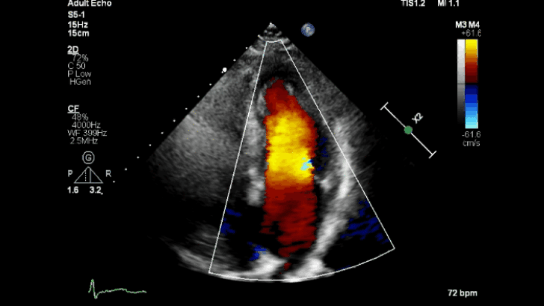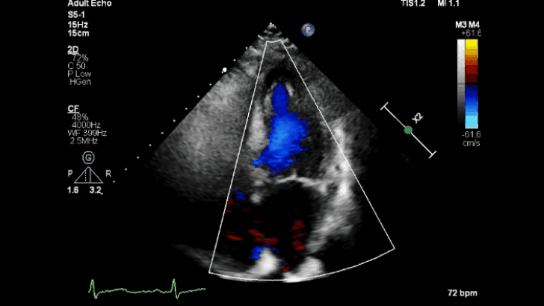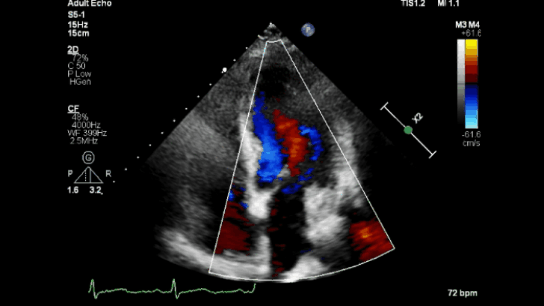

Spectral Doppler

CW (Continuous wave)
Continuous wave Doppler technology transmits and receives sound waves using separate piezoelectric crystals. It measures flow velocity along a defined path, capturing both direction and speed, even at high velocities. However, it does not identify the specific locations of individual velocity elements.

PW (Pulsed wave)
In pulsed wave Doppler, the user defines a small area, or "gate," within the B-mode image. Only the Doppler shifts from this area are recorded using pulse repetition frequency. While it avoids the range ambiguity of continuous wave Doppler, pulsed wave Doppler is susceptible to aliasing at higher velocities, especially for targets farther from the transducer.
Power Doppler

Ultrasound power Doppler (PD) joint inflammation. Example of a sonogram (longitudinal view) showing grade 2 PD joint inflammation at the metacarpophalangeal joint (arrows pointing towards PD vascularity).
Diagnostics 2024, 14(21), 2384;
https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14212384
Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
